Researchers from the University of Basel, the Swiss Nanoscience Institute (SNI) and University of Hanover have succeeded in creating strong coupling between quantum systems over a great distance. They accomplished this with a novel method in which a laser loop connects the systems, enabling nearly lossless exchange of information and strong interaction between them. This new method opens up new possibilities in quantum networks and quantum sensor technology.
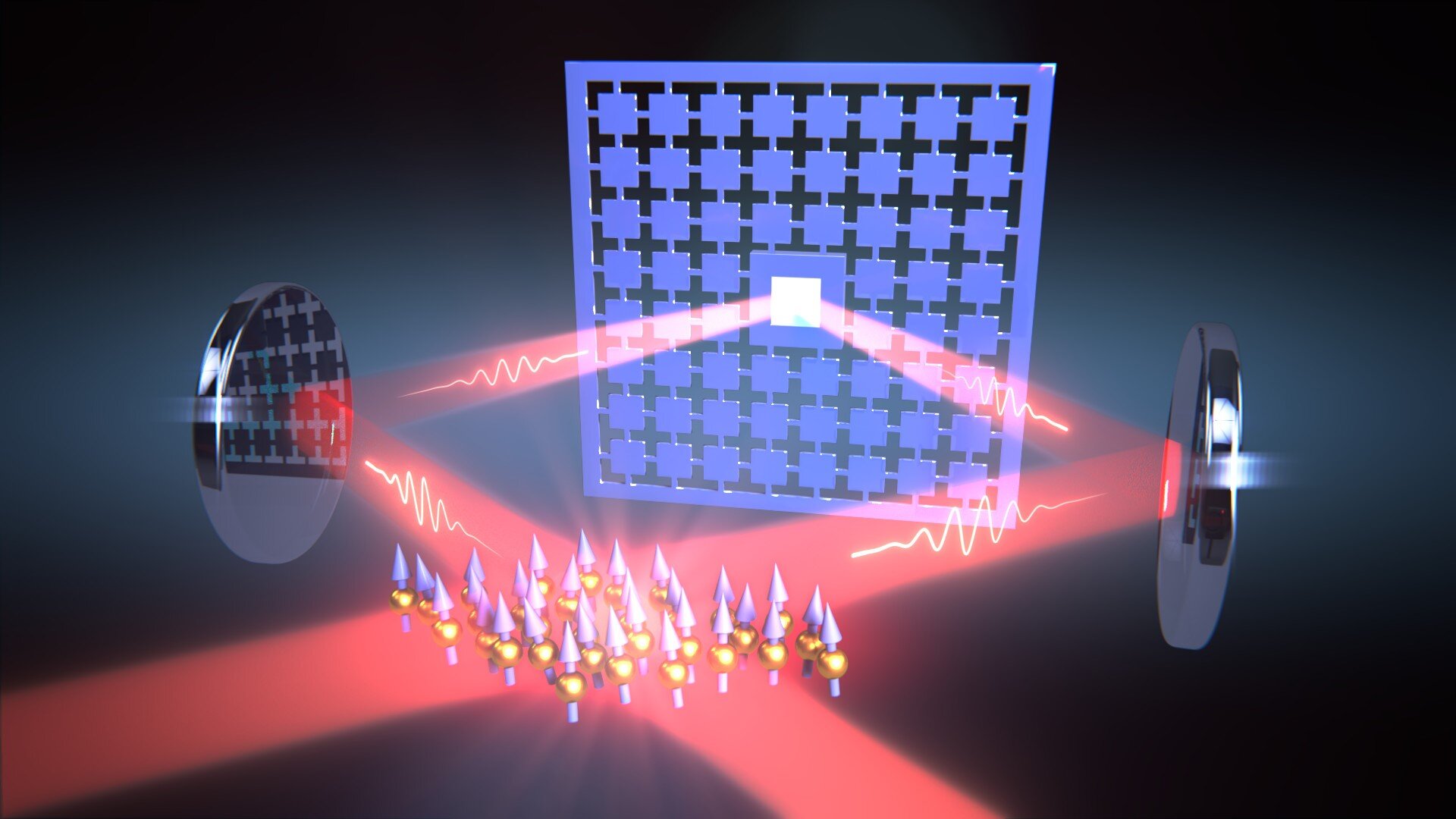
In their experiment, the researchers used laser light to couple the vibrations of a 100 nm thin membrane to the motion of the spin of atoms over a distance of one meter. As a result, each vibration of the membrane sets the spin of the atoms in motion and vice versa.
The concept involves sending a beam of laser light back and forth between the systems. In this laser loop, the properties of the light can be controlled such that no information about the motion of the two systems is lost to the environment, thus ensuring that the quantum mechanical interaction is not disturbed.
In addition to coupling atoms with nano-mechanical membranes, the new method might also be used in several other systems. For example, when coupling superconducting quantum bits or solid-state spin systems used in quantum computing research. The new technique for light-mediated coupling could be used to interconnect such systems, creating quantum networks for information processing and simulations.
The study has been reported in the journal Science.
