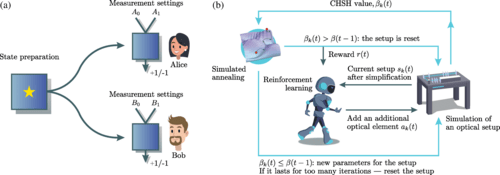
Terra Quantum, a Swiss startup, and University of Basel have developed a combination of reinforcement learning and simulated annealing for setting up efficient Bell tests useful for quantum cryptography.
Finding optical setups producing measurement results with a targeted probability distribution is hard, as a priori the number of possible experimental implementations grows exponentially with the number of modes and the number of devices.
To tackle this complexity, they introduced a method combining reinforcement learning and simulated annealing enabling the automated design of optical experiments producing results with the desired probability distributions.
They illustrated the relevance of our method by applying it to a probability distribution favouring high violations of the Bell-Clauser-Horne-Shimony-Holt (CHSH) inequality.
As a result, they have proposed new unintuitive experiments leading to higher Bell-CHSH inequality violations than the best currently known setups.
Their method might positively impact the usefulness of photonic experiments for device-independent quantum information processing.
The paper has been published in Physical Review Letters.
